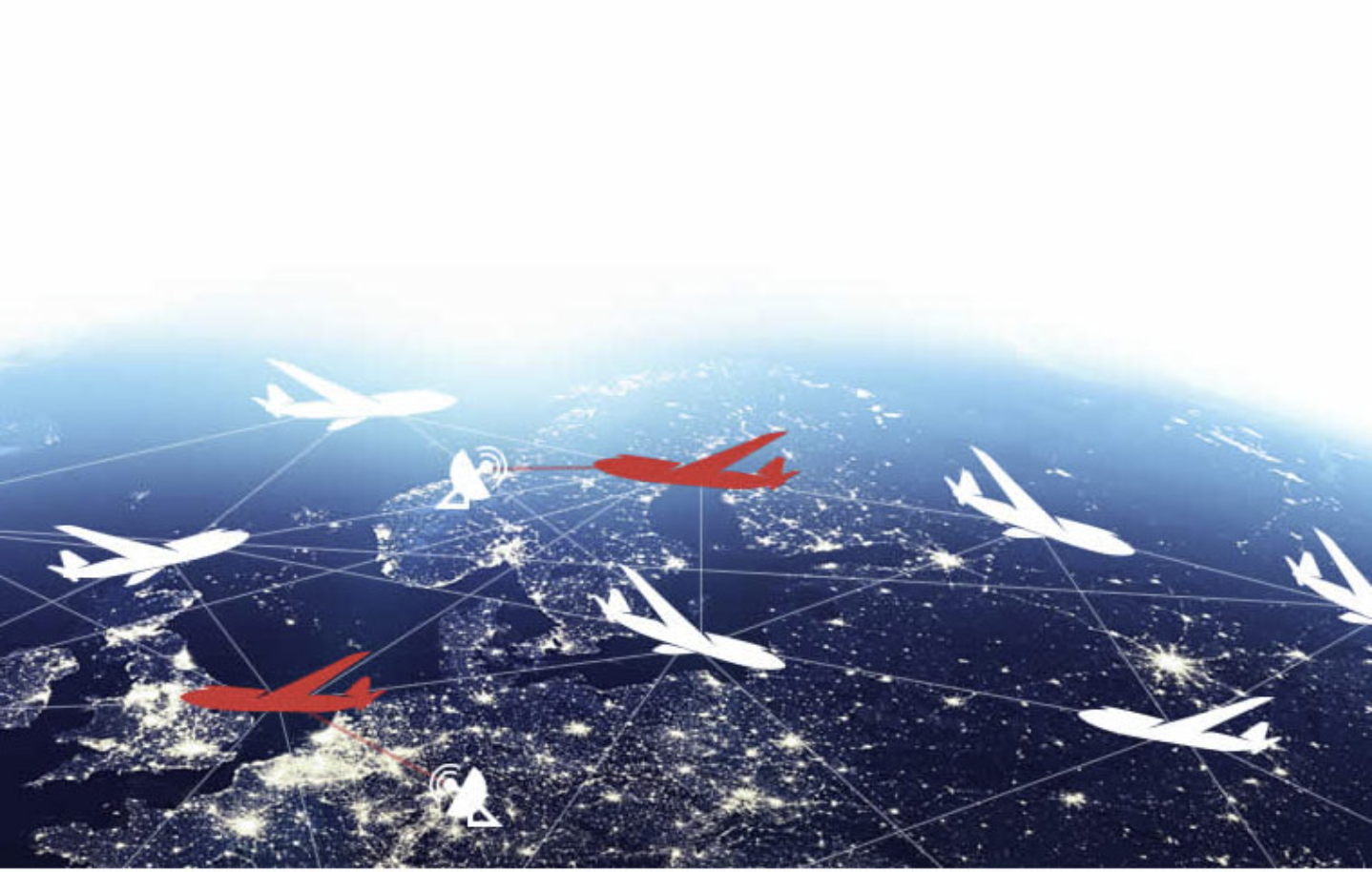
Airborne Internet is a proposed system that would provide an integrated digital data network connecting aircraft with the ground, offering an alternative to traditional broadband and wireless connections. In this system, aircraft act as nodes or points for transmitting Internet data, potentially changing how air traffic control monitors and communicates with planes, as well as how they exchange information with other aircraft.
The idea of airborne internet emerged as the aviation industry began to explore the use of computer networking principles. Initially supported by NASA’s small aircraft transportation system, the main goal of airborne internet technology is to establish a reliable communication link between aircraft and the ground. This innovation not only enhances communication but also boosts the productivity of both the aviation and transportation sectors. As the system evolves, its capabilities are expected to expand significantly, offering numerous benefits, though it also has its drawbacks.
Airborne internet aims to provide a stable and accessible data connection to aircraft, similar to how a computer is connected to a local or global network. Since aircraft are constantly moving, the system must support mobile routing to maintain a continuous data connection as the plane moves between regions. This mobile routing technology, along with updates to the Internet protocol (IP), ensures that the network can accommodate the growing demand for wireless devices that can easily move between networks.
Several companies are already working on airborne internet technologies. One notable example is Angel Technologies, which uses its Proteus aircraft, equipped with wireless networking gear and a one-ton aerial network hub. This hub transmits data from ground stations to users on the ground through an array of antennas that create virtual ground cells, much like mobile phone towers. These cells support multiple users, allowing data to be transmitted efficiently. Powered by solar energy and fuel cells, the aircraft’s communication system mirrors high-speed data transmission from ground stations.
Another player, Sky Station International, is working on lighter-than-air platforms such as blimps, which are designed to provide wireless internet connectivity from the sky. These blimps will hover above at least 250 cities globally, offering internet coverage to a large area. With fuel cells and solar panels powering the blimps, they aim to provide wireless broadband connections, offering a reliable, high-speed internet service.
NASA is also developing its own version of airborne internet technology, focusing on solar-powered, lightweight aircraft capable of hovering at high altitudes for extended periods. These aircraft, in collaboration with AeroVironment, will transport broadband connections from the sky. While still in the prototype stage, the project aims to create a long-duration airborne communication system.
The benefits of airborne internet are significant. It reduces the cost of both ground-based and aerial equipment, improving communication between aircraft, air traffic control, and ground services. By providing additional bandwidth, it can even support aircraft that require minimal data. The system also offers global connectivity, ensuring better connections for users around the world. Additionally, it allows passengers to use their travel time productively by accessing the internet while in transit.
Despite its many advantages, airborne internet has some challenges. Each aircraft in the system will act as a network node, responsible for sending, receiving, and processing data through distributed routes. These nodes need to be designed to handle mobile routing and prevent network disconnections as the plane moves through different regions. The system will rely on high-speed digital networks and packet-switching technology, with antennas on the aircraft communicating with multiple beams to ensure a stable connection. Users will typically have access to broadband channels, allowing them to use the internet on the go.
In conclusion, airborne internet is an emerging technology that could revolutionize communication in the skies, providing faster, more reliable internet connections for aircraft and passengers alike. However, its development requires overcoming technical challenges related to mobile routing and the construction of a robust digital network. As this technology matures, it promises to enhance connectivity and efficiency in the aviation and transportation industries.