Overview of Network Design and Architecture
Network architecture and design are key to building strong, secure, and effective communication systems. In this guide, we’ll explore the complexity of network design, look into the principles that shape it, examine different network topologies, and offer best practices for creating scalable and reliable networks.
Understanding Network Architecture
At its core, network architecture defines how a network is built, organized, and managed. It focuses on how data is routed and transmitted, making it essential to design communication systems with these key components:
- Network Components: These are the building blocks of a network, including servers, routers, switches, firewalls, and access points. Each plays a vital role in resource access, security enforcement, and data transmission.
- Network Protocols: Protocols like TCP/IP, UDP, HTTP, and DNS control how data is formatted, transmitted, and received. Understanding these ensures smooth communication across devices and systems.
- Addressing and Naming: Devices on a network are identified through IP addresses and DNS (Domain Name System). These elements make it possible to locate and communicate with devices, ensuring smooth data exchange.
- Network Services: Services like DHCP, NAT, and VPN provide critical functions such as IP address allocation, address translation, and secure communication. These services help optimize performance and enhance security, reducing risks and improving the overall user experience.
Key Design Principles
Effective network design relies on several key principles to optimize security, performance, scalability, and reliability:
- Scalability: Networks should be able to handle growth in users, devices, and traffic without losing performance. A scalable network architecture uses modular components and hierarchical structures to allow for easy expansion.
- Redundancy: Redundancy involves having backup components, links, and pathways in place so that the network can continue to operate if something fails. This helps ensure high availability and reduces downtime.
- Resilience: Resilient networks are built to recover quickly from failures. This is achieved with techniques like load balancing, route diversification, and fast recovery protocols, ensuring minimal disruption and continuous service.
- Security: Security is a top priority in network design. Measures such as access control, encryption, intrusion detection, and secure configurations protect the network from unauthorized access and cyber threats, maintaining the integrity of the system.
- Simplicity: Simple designs are easier to scale, manage, and troubleshoot. Sticking to standardized architectures reduces errors, simplifies operations, and boosts overall efficiency.
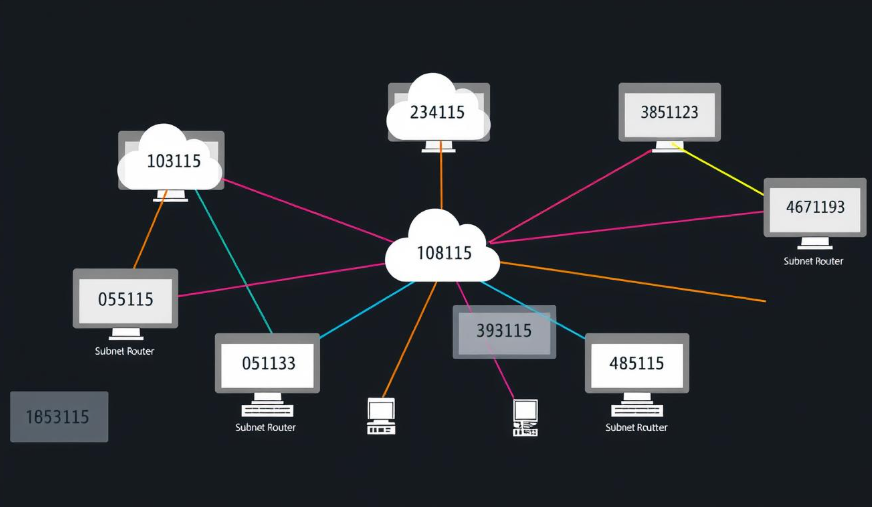
Network Topologies
Network topology refers to the arrangement of devices and connections in a network. Different topologies offer various advantages in terms of scalability, fault tolerance, and cost-effectiveness:
- Star Topology: In this setup, all devices connect to a central hub or switch. It’s easy to set up and allows for centralized management, but the central hub can become a single point of failure.
- Mesh Topology: This topology provides multiple paths between devices, ensuring redundancy and fault tolerance. However, it can be expensive and complex to implement and maintain.
- Bus Topology: Devices in a bus topology are connected to a single backbone. It’s affordable and simple, but it has limited scalability and can suffer from congestion and data collisions.
- Ring Topology: Devices are connected in a closed loop, and data travels in one direction. It’s efficient in terms of bandwidth usage, but it can be prone to bottlenecks and single points of failure.
Best Practices for Network Design
To create secure and effective networks, it’s crucial to follow best practices in the design process:
- Modular Design: By breaking the network into smaller, manageable modules, it becomes more flexible and easier to maintain and scale.
- Documentation: Comprehensive documentation of network architecture, configurations, and policies is essential for troubleshooting, managing changes, and sharing knowledge among network administrators.
- Regular Audits and Assessments: Conducting regular reviews helps identify vulnerabilities, performance issues, and areas for improvement, allowing for proactive optimization.
- Adherence to Standards: Following industry standards ensures compatibility, regulatory compliance, and interoperability, improving network reliability and performance.
- Testing and Validation: Thorough testing and validation of network designs and security measures before deployment help identify potential issues and reduce risks.
Conclusion
Network architecture and design are the foundation of any communication system, affecting its security, performance, and reliability. By understanding the core principles, choosing the right topologies, and following best practices, organizations can build strong, scalable, and secure networks that meet the demands of today’s digital world.